There are n computers numbered from 0 to n-1 connected by ethernet cables connections forming a network where connections[i] = [a, b] represents a connection between computers a and b. Any computer can reach any other computer directly or indirectly through the network.
Given an initial computer network connections. You can extract certain cables between two directly connected computers, and place them between any pair of disconnected computers to make them directly connected. Return the minimum number of times you need to do this in order to make all the computers connected. If it's not possible, return -1.
Example 1:

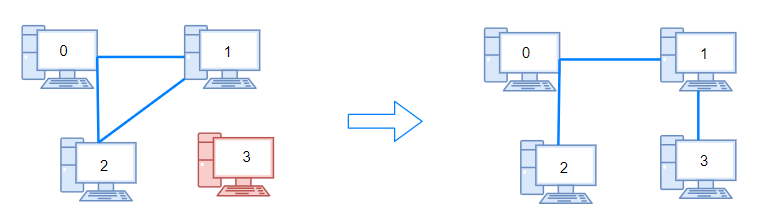
Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Remove cable between computer 1 and 2 and place between computers 1 and 3.
Number of Operations to Make Network Connected - LeetCode
Goal: We need to connect all the computers (directly or indirectly). We have to return the minimum number of operations that are required to connect the computers. An operation consists of removing a cable between two directly connected computers and put it between two disconnected computers.
This problem is a simple variation of counting the number of islands.
We know that the minimum number of edges required for a graph with n nodes to remain connected is n - 1. Similarly, if there are k components in a disconnected graph, then we need at least k - 1 edges to connect every component.
With that in our mind, we will start with our base condition. If the number of edges in the graph is greater than n - 1 or not. If not, we will return -1.
Next, we will count the number of components (k). As I already mentioned, we will need k - 1 operations to connect the computers (components). And that is our answer!
Using Kosaraju Algorithm
class Solution {
public:
stack <int> st;
int makeConnected(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
int nc = connections.size();
if(nc<n-1)
return -1;
vector<int> adj[n];
for(auto connection:connections) // Preparing the adj list for undirected graph
{
adj[connection[0]].push_back(connection[1]);
adj[connection[1]].push_back(connection[0]);
}
vector<bool> visited(n,false);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) // Step 1: Calling the DFS1 func to fill up the stack
{
if(!visited[i])
dfs1(i,adj,visited);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Step 2: Here we do not need to reverse the edges as it is an undirected graph
int scc = 0;
while(!st.empty()) // Step 3 : Calling DFS2 function to count the SCCs
{
int u = st.top();
st.pop();
if(!visited[u])
{
dfs2(u,adj,visited);
scc++;
}
}
return scc-1;
}
void dfs1(int u,vector<int> adj[],vector<bool> &visited)
{
if(visited[u])
return;
visited[u] = true;
for(int v:adj[u])
dfs1(v,adj,visited);
st.push(u);
}
void dfs2(int u,vector<int> adj[],vector<bool> &visited)
{
if(visited[u])
return;
visited[u] = true;
for(int v:adj[u])
dfs2(v,adj,visited);
}
};
Using Normal DFS
class Solution {
public:
stack<int> st;
vector<int> visited;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
int scc = 0;
void dfs(int u)
{
if(visited[u])
return;
visited[u] = true;
for(int v:adj[u])
{
if(!visited[v])
{
dfs(v);
}
}
}
int makeConnected(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
int nc = connections.size();
if(nc<n-1)
return -1;
adj.resize(n);
visited.resize(n,false);
for(auto c:connections)
{
adj[c[0]].push_back(c[1]);
adj[c[1]].push_back(c[0]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(!visited[i])
{
dfs(i);
scc++;
}
}
return scc-1;
}
};