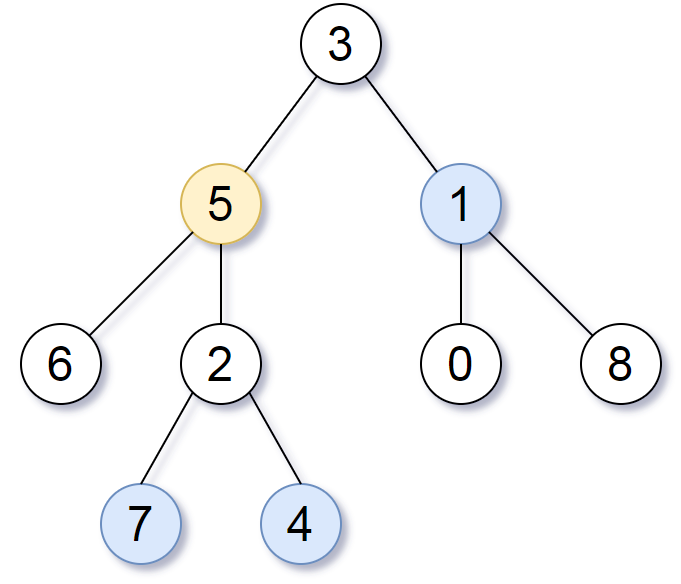
Given the root of a binary tree, the value of a target node target, and an integer k, return an array of the values of all nodes that have a distance k from the target node.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, k = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 1, k = 3
Output: []
Constraints:
[1, 500].0 <= Node.val <= 500Node.val are unique.target is the value of one of the nodes in the tree.0 <= k <= 1000All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree - LeetCode
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,unordered_set<int>> adj;
void preorder(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)
return;
if(root->left)
{
adj[root->val].insert(root->left->val);
adj[root->left->val].insert(root->val);
}
if(root->right)
{
adj[root->val].insert(root->right->val);
adj[root->right->val].insert(root->val);
}
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int k) {
preorder(root);
queue<int> q;
vector<int> visited(501,false);
q.push(target->val);
visited[target->val] = true;
int depth = 0;
vector<int> res;
while(!q.empty())
{
int lsize = q.size();
while(lsize--)
{
int curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if(depth>k)
return res;
if(depth==k)
res.push_back(curr);
for(int v:adj[curr])
{
if(visited[v])
continue;
visited[v] = true;
q.push(v);
}
}
depth++;
}
return res;
}
};